Starting with Ethereum and Ethereum Classic, the landscape of blockchain technology takes on new dimensions, capturing the interest of enthusiasts and investors alike. These two platforms, originating from a shared vision, have evolved in distinct ways, showcasing unique features and functionalities that cater to different segments of the market.
As we delve deeper into their histories, technological differences, and community dynamics, we will uncover how each network has carved its own niche in the ever-changing blockchain ecosystem and what lies ahead for both.
Overview of Ethereum and Ethereum Classic
Ethereum and Ethereum Classic both arise from the same initial vision of creating a decentralized platform for building applications without the need for intermediaries. Launched in July 2015, Ethereum was designed by Vitalik Buterin and his team, aiming to extend the blockchain concept beyond cryptocurrency to include smart contracts. However, following a notable hack in 2016 involving a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that raised over $150 million in Ether, the Ethereum community faced a critical decision.
The split that ensued led to the creation of Ethereum Classic, which continues to uphold the original code and ideology of immutability.The primary differences between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic stem from their approach to governance and updates. While Ethereum has embraced upgrades and changes to enhance scalability and functionality, Ethereum Classic remains committed to its original codebase. This ideological rift has fostered distinct communities and varied development paths for both networks.
- 2015: Ethereum launches, enabling smart contracts and decentralized applications.
- 2016: The DAO hack occurs, resulting in significant losses for investors.
- July 2016: Ethereum undergoes a hard fork to reverse the DAO hack, creating Ethereum.
- July 2016: Ethereum Classic is born, preserving the original blockchain.
- 2020: Ethereum 2.0 transition begins, shifting towards proof-of-stake.
Technological Differences
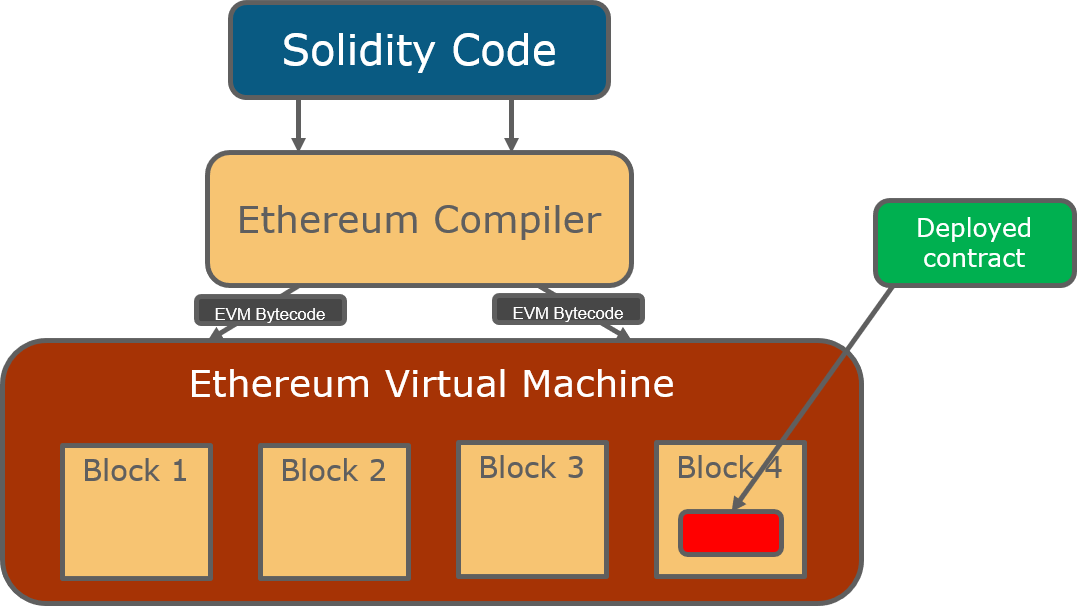
The technological underpinnings of Ethereum and Ethereum Classic showcase significant contrasts, particularly in their consensus mechanisms. Ethereum transitioned to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus with the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which aims to enhance scalability and reduce energy consumption significantly. In contrast, Ethereum Classic continues to utilize the proof-of-work (PoW) model, mirroring Bitcoin’s initial approach to securing the network.
Consensus Mechanisms
Ethereum’s PoS mechanism allows validators to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral. This shift not only makes the network more energy-efficient but also encourages long-term holding among investors. On the other hand, Ethereum Classic’s PoW relies on miners who solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and secure the network, which consumes more energy and resources.
Smart Contracts Comparison
Ethereum’s smart contracts are more advanced and versatile, benefiting from a wide range of developer tools and frameworks that enhance their functionality. The Ethereum ecosystem supports various programming languages, notably Solidity, which is specifically designed for writing smart contracts. Ethereum Classic supports smart contracts as well but lacks the extensive developer resources that Ethereum offers, limiting its ecosystem growth.
Notable Projects
Examples of notable projects on Ethereum include:
- Uniswap – A decentralized finance (DeFi) protocol for swapping various cryptocurrencies.
- Chainlink – A decentralized oracle network that provides real-world data to smart contracts.
- Axie Infinity – A blockchain-based game where players can earn cryptocurrency through gameplay.
On Ethereum Classic, key projects include:
- ClassicEtherWallet – A popular wallet for managing Ether and tokens on Ethereum Classic.
- Ethereum Classic Labs – An organization focused on developing and promoting Ethereum Classic.
Use Cases and Applications
Ethereum has established itself as a powerhouse for real-world applications across various industries. With its versatile smart contract capabilities, Ethereum supports a myriad of use cases. For instance, countless decentralized applications (dApps) have emerged, addressing needs in finance, gaming, supply chain, and more.
Real-World Applications on Ethereum
Examples include:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) applications like Aave and Compound that allow users to borrow, lend, and earn interest on cryptocurrencies.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), with platforms like OpenSea that enable the buying and selling of digital art and collectibles.
- Supply Chain solutions that enhance transparency and traceability, such as VeChain.
Use Cases of Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic maintains its relevance within the blockchain ecosystem, particularly for applications prioritizing immutability. Its most notable use cases include:
- Digital asset management platforms that leverage the security of an unaltered blockchain.
- Decentralized applications focused on maintaining a consistent and reliable ledger.
Industries Impacted
Both technologies have significantly impacted finance, gaming, supply chain management, and digital art sectors, solidifying blockchain’s role in these industries.
Community and Governance
The communities supporting Ethereum and Ethereum Classic are distinct, with different philosophies regarding governance and development. Ethereum’s community is more centralized, utilizing a core team to implement upgrades and changes based on community feedback. This collaborative approach fosters innovation but can also lead to disagreements over future directions.
Community Support
Ethereum boasts a larger and more active community, with numerous developers and enthusiasts contributing to its ecosystem. Events like Devcon and regular hackathons encourage engagement and collaboration. Conversely, Ethereum Classic’s community is smaller but fiercely dedicated to preserving its original vision, emphasizing immutability and resistive to changes.
Governance Differences
Governance structures differ significantly, with Ethereum adopting a more flexible approach that allows for quick implementation of updates. In contrast, Ethereum Classic adheres to a strict governance model that requires broad consensus for any changes, reflecting its commitment to the principles of immutability.
Development Roadmaps
Ethereum’s development roadmap includes ambitious plans for scalability upgrades, such as sharding and Layer 2 solutions. Ethereum Classic focuses on maintaining stability and security, with an emphasis on supporting existing projects and improving their performance.
Market Performance and Investment
Analyzing the market performance of Ethereum and Ethereum Classic reveals divergent trends over the past few years. Ethereum has consistently ranked among the top cryptocurrencies by market capitalization, driven by its dynamic ecosystem and broad adoption across various sectors.
Market Trends
Ethereum has witnessed substantial growth, particularly with the rise of DeFi and NFTs, driving its price to new highs. In contrast, Ethereum Classic has experienced more volatility, often influenced by external market factors and its comparatively smaller user base.
Market Capitalization Comparison
As of the latest data, Ethereum’s market capitalization significantly surpasses that of Ethereum Classic, reflecting the broader adoption and user engagement with its network. This disparity highlights the potential investment risks associated with Ethereum Classic, which, while maintaining loyal support, lacks the same level of institutional interest.
Investment Potential and Risks
Investors considering Ethereum are generally drawn by its growth potential and extensive use cases. However, risks include market volatility and regulatory scrutiny. For Ethereum Classic, while it offers a platform for immutable transactions, its smaller market and potential stagnation pose investment challenges that need careful consideration.
Future Prospects
The future of Ethereum is bright, with upcoming upgrades expected to significantly enhance its scalability and user experience. The transition to a fully operational proof-of-stake system is anticipated to reduce transaction fees and improve network efficiency, attracting more users and projects.
Challenges Facing Ethereum Classic
Ethereum Classic, while robust in its principles, faces challenges including adoption stagnation and competition from other platforms. Its commitment to immutability may hinder necessary innovations that could attract new projects and investments.
Trends in the Blockchain Industry
Emerging trends in the blockchain industry, such as increased regulatory scrutiny and the rise of Layer 2 solutions, will impact both platforms. As more industries explore blockchain integration, the ability to adapt and innovate will be crucial for sustaining relevance in the fast-evolving landscape.
Security and Risks
Security is paramount in the world of blockchain, and both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic have implemented various measures to protect their networks. Ethereum’s ongoing transition to proof-of-stake is designed to enhance security while reducing energy consumption, thereby bolstering investor confidence.
Security Measures
Both platforms utilize cryptographic techniques and decentralized networks to secure transactions. Ethereum has invested heavily in audit frameworks and testing to preemptively address vulnerabilities. Ethereum Classic, retaining its PoW model, continues to prioritize miner security to prevent double-spending and potential attacks.
Historical Hacks and Breaches
The DAO hack in 2016 remains a significant event in Ethereum’s history, leading to the hard fork that created Ethereum Classic. Ethereum Classic has also faced its share of security challenges, including a notorious 51% attack in 2020, which raised concerns about its network security and resilience.
Risk Assessment for Investors
Investors considering either cryptocurrency must weigh the potential rewards against inherent risks. For Ethereum, the rapid pace of development and community engagement offers promising opportunities, though market volatility remains a concern. In contrast, Ethereum Classic’s commitment to immutability presents a unique investment narrative but is tempered by its smaller ecosystem and historical vulnerabilities.
Developer Ecosystem
The developer ecosystem is a crucial factor for the success of any blockchain platform, and both Ethereum and Ethereum Classic offer various resources and support for developers.
Resources for Developers

Ethereum provides a comprehensive suite of tools and frameworks, including Truffle and Hardhat, facilitating smart contract development and testing. Extensive documentation, tutorials, and community support help new developers to quickly get started. In contrast, Ethereum Classic offers basic resources, but the smaller community means fewer comprehensive tools available for developers.
Ease of Development
Developing on Ethereum is generally viewed as more accessible due to its extensive resources and community support. Ethereum Classic, while functional, poses more challenges due to limited developer tools and a narrower community, making it less appealing for new projects.
Developer Engagement Initiatives

Ethereum actively promotes developer engagement through hackathons, grants, and educational programs, fostering a vibrant ecosystem. Ethereum Classic, while less active in outreach, supports developers through its community initiatives, emphasizing the importance of maintaining its original values.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the journey through Ethereum and Ethereum Classic reveals not only their individual strengths and challenges but also highlights the broader implications for the blockchain industry. With ongoing developments and a dynamic market landscape, both platforms are poised to play significant roles in shaping the future of decentralized applications and smart contracts.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the main difference between Ethereum and Ethereum Classic?
The primary difference lies in their governance; Ethereum continues to evolve with a focus on upgrades, while Ethereum Classic adheres strictly to its original code post-split.
Can I use Ethereum Classic for smart contracts?
Yes, Ethereum Classic supports smart contracts, but they may not have the same extensive features as those on Ethereum.
Is Ethereum or Ethereum Classic a better investment?
Investment potential varies; Ethereum is generally viewed as having higher growth prospects due to ongoing developments, while Ethereum Classic appeals to those valuing stability and adherence to original principles.
How do both platforms handle security?
Both platforms employ robust security measures, but their histories differ, with Ethereum experiencing more significant hacks that have shaped its security protocols.
What notable projects are built on Ethereum Classic?
Some noteworthy projects include the Classic Ether Wallet and various decentralized applications that prioritize the original ethos of decentralization.