Ethereum algorithm name serves as a pivotal element in the blockchain landscape, revolutionizing how transactions are conducted and recorded.
As we delve into the intricacies of Ethereum, we uncover the various algorithms that power its functionality, the consensus mechanisms that ensure reliability, and the innovative smart contracts that have made Ethereum a cornerstone of decentralized applications.
Understanding Ethereum and Its Algorithms

Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that allows developers to build and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Its significance in blockchain technology lies in its ability to facilitate complex transactions without the need for intermediaries, thus enhancing transparency and security. As one of the most widely used blockchain platforms, Ethereum has set the stage for the development of decentralized finance (DeFi) and other innovative applications.Ethereum utilizes a variety of algorithms to ensure its functionality.
At its core, the platform relies on consensus algorithms to validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain. Additionally, Ethereum employs the Ethash algorithm for mining, which is designed to be memory-hard, making it resistant to ASIC dominance. When comparing Ethereum’s algorithms with those of other blockchains, such as Bitcoin’s SHA-256, it’s clear that Ethereum prioritizes decentralization and accessibility.
The Ethereum Consensus Mechanism
The consensus mechanism in Ethereum has evolved significantly over time. Initially, Ethereum utilized Proof of Work (PoW), similar to Bitcoin, which requires miners to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. This method, while secure, can be energy-intensive and slow. In contrast, the introduction of Proof of Stake (PoS) in Ethereum 2.0 aims to address these issues by allowing validators to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.The transition from PoW to PoS is not just a technical upgrade; it fundamentally changes how transactions are processed.
PoS can significantly increase transaction speeds while enhancing network security. This shift is expected to reduce energy consumption and make Ethereum more environmentally sustainable.
Ethereum Algorithm: Ethash
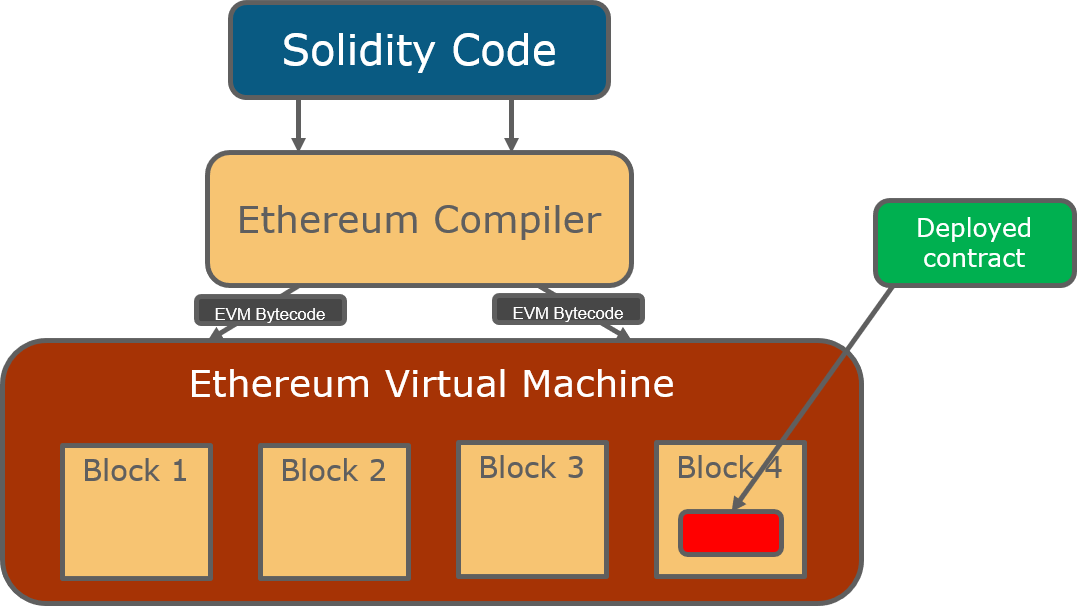
Ethash is the algorithm used in Ethereum’s mining process, characterized by its memory-hard design. This means it requires significant amounts of memory to compute, which helps to level the playing field for miners by reducing the effectiveness of ASIC miners. Ethash promotes decentralized mining and encourages a wider range of hardware to participate, which is essential for maintaining Ethereum’s decentralized nature.While Ethash has its strengths, such as promoting decentralization and being ASIC-resistant, it also has weaknesses.
The memory-intensive nature of the algorithm can lead to increased energy consumption and slower mining speeds compared to ASIC-focused alternatives.
The Role of Smart Contracts in Ethereum’s Algorithm
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. In the Ethereum ecosystem, these contracts function as automated agreements that execute actions based on predefined conditions. The underlying algorithms, including Ethash, facilitate the secure execution and validation of these contracts, ensuring that all parties adhere to the terms without the need for intermediaries.Examples of successful smart contracts include decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs), which have generated significant interest and market activity.
The impact of these smart contracts on the Ethereum network has been profound, fostering innovation and creating new economic models.
Future Developments in Ethereum Algorithms
Ethereum 2.0 is set to bring several algorithm changes and enhancements that will improve scalability and efficiency. These updates aim to address the challenges faced by the network, such as high transaction fees and congestion. Potential solutions include sharding, which will allow the network to process multiple transactions simultaneously, enhancing overall performance.A roadmap for these future improvements includes the implementation of PoS, the introduction of shard chains, and ongoing optimizations to existing algorithms.
These advancements are expected to significantly enhance Ethereum’s usability and adaptability in the rapidly changing blockchain landscape.
Analyzing Ethereum’s Ecosystem and Forks
Hard forks are a crucial aspect of Ethereum’s evolution, often resulting from disagreements within the community regarding algorithm changes. These forks can create separate versions of the blockchain, each with its own set of rules and algorithms. Major Ethereum forks, such as Ethereum Classic, have introduced new algorithms and changes in governance, which have led to varying degrees of community support and market performance.The impact of these forks on the Ethereum community is substantial, as they can lead to shifts in user engagement, development focus, and market dynamics.
Understanding the relationship between these forks and algorithm changes is essential for grasping Ethereum’s ongoing development.
Practical Applications of Ethereum Algorithms

Ethereum’s algorithms underpin a wide array of real-world applications, showcasing the platform’s versatility and potential. From decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to supply chain management solutions, the use cases are diverse and impactful.Case studies of successful Ethereum-based projects, such as Uniswap and MakerDAO, demonstrate the effectiveness of these applications. Developers play a critical role in creating and optimizing applications that leverage Ethereum’s algorithms effectively, contributing to the platform’s growth and innovation.
By continuously improving their projects, developers help to expand the boundaries of what is possible within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Epilogue
In summary, understanding the Ethereum algorithm name not only sheds light on how this blockchain operates but also highlights its potential for future developments and practical applications that could reshape technology and finance.
General Inquiries
What is the main purpose of the Ethereum algorithm?
The Ethereum algorithm is designed to facilitate decentralized applications and smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
How does the Ethash algorithm support mining?
Ethash promotes decentralized mining by allowing more participants to engage, thereby reducing reliance on specialized mining hardware.
What are the benefits of transitioning to Proof of Stake?
Transitioning to Proof of Stake enhances energy efficiency, increases security, and speeds up transaction processing.
How do hard forks affect Ethereum’s algorithms?
Hard forks can result in significant changes to Ethereum’s algorithms, affecting functionality and user experience while also creating new versions of the blockchain.
What are some practical applications of Ethereum algorithms?
Ethereum algorithms enable a range of applications, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs), showcasing their versatility and impact.